Mouse Identification Guide

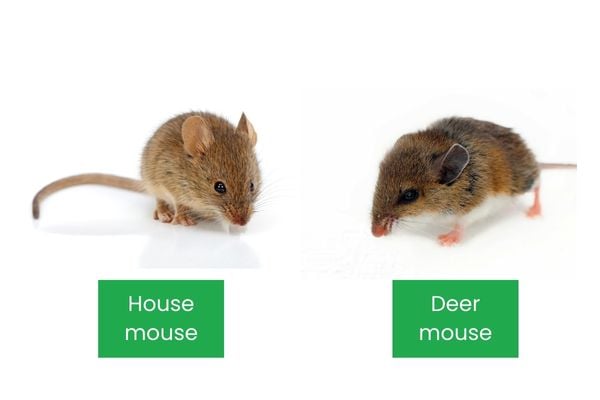
Mice Characteristics


Mouse Inspection Guide
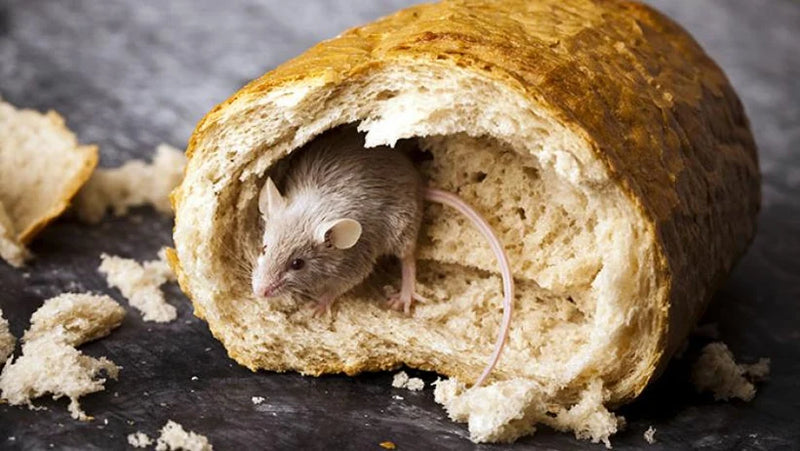
Step1 Signs of Mice
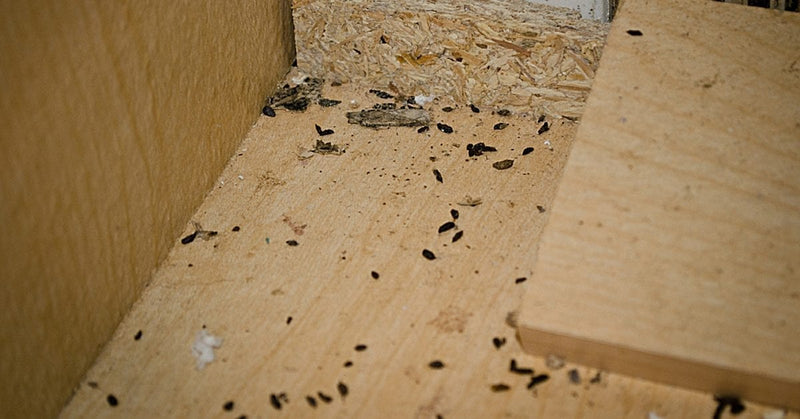
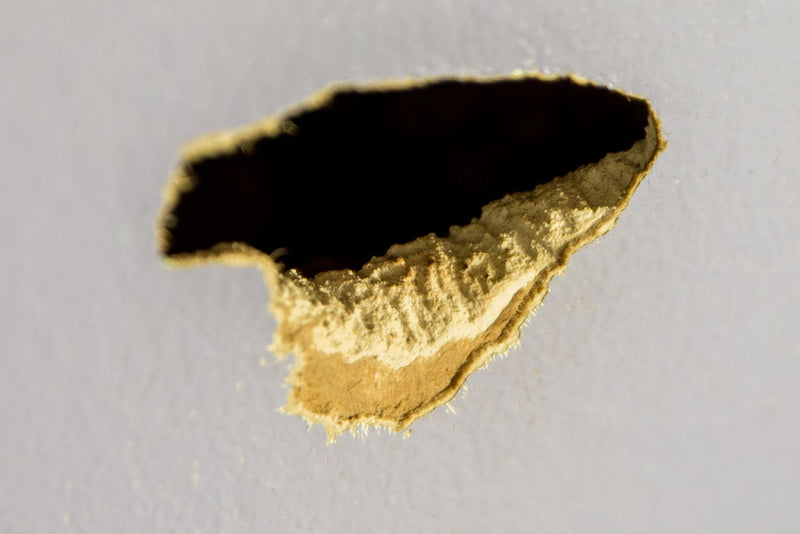



How to Eliminate Mice

Step1 Sanitation
Step2 Catching & Removing Mice









