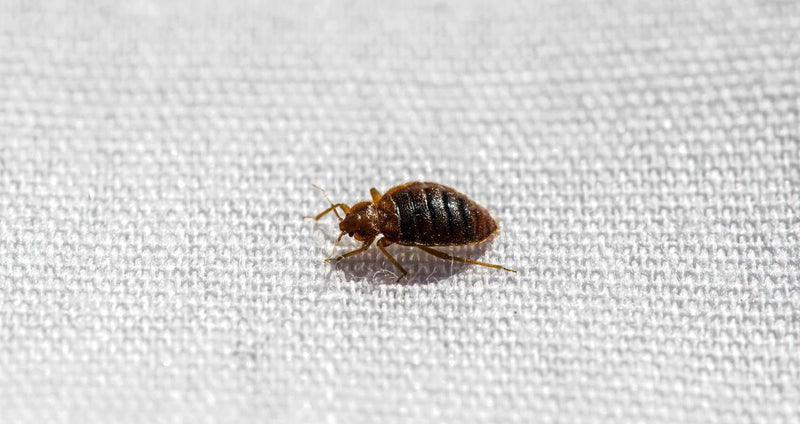
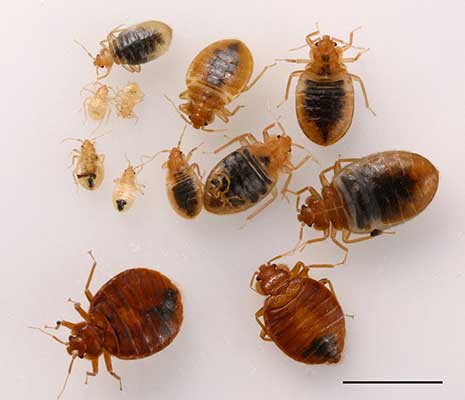
What Do Bed Bugs Look Like?

Characteristics of Bed Bugs | Size

Characteristics of Bed Bugs | Shape
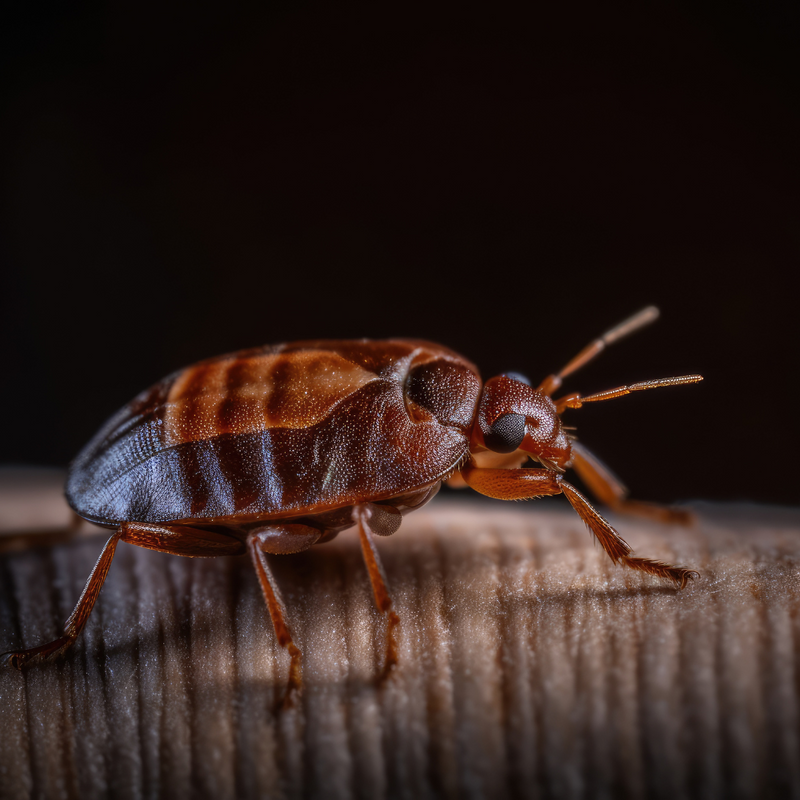
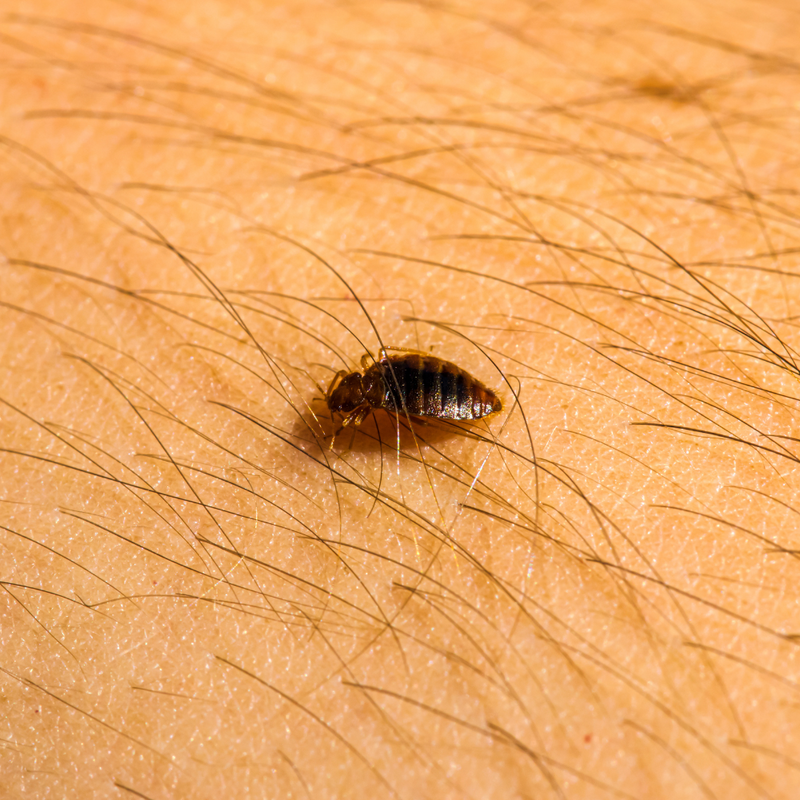



Characteristics of Bed Bugs | Color

Recommended Products
Bed Bugs - Range
How to Check for Bed Bugs
Recommended Products
Step1 Check Common Bed Bug Hiding Spots
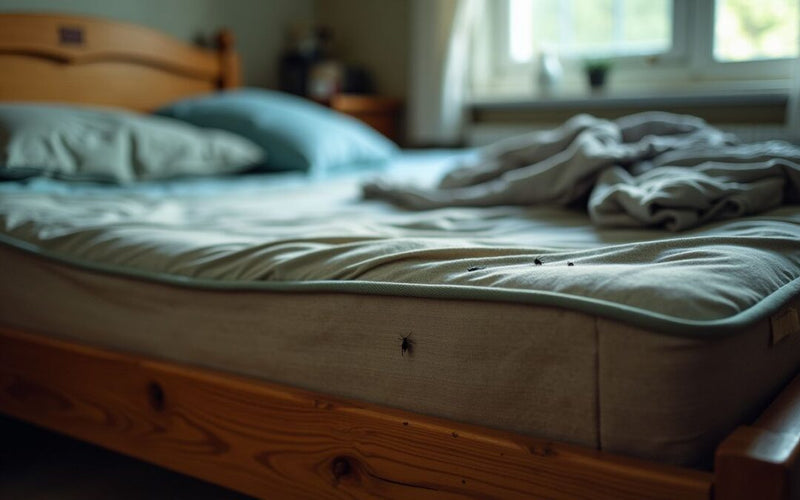
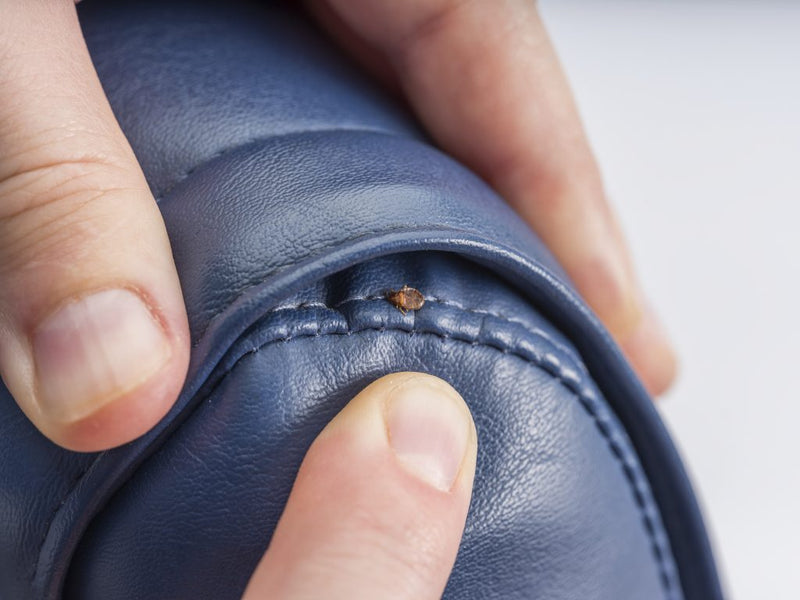
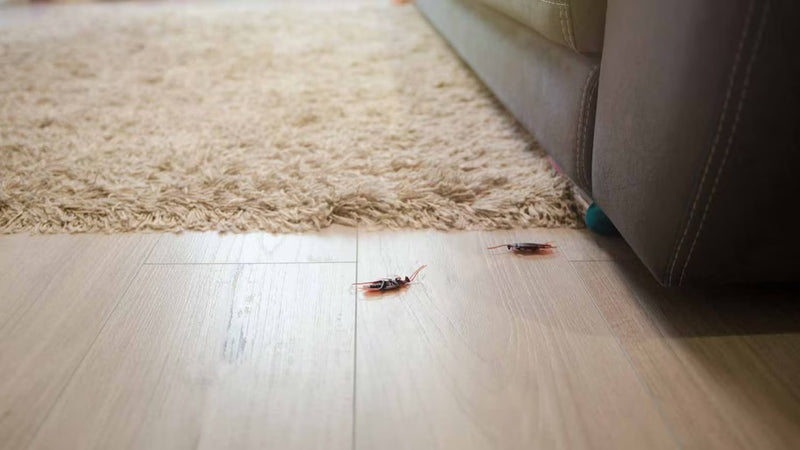



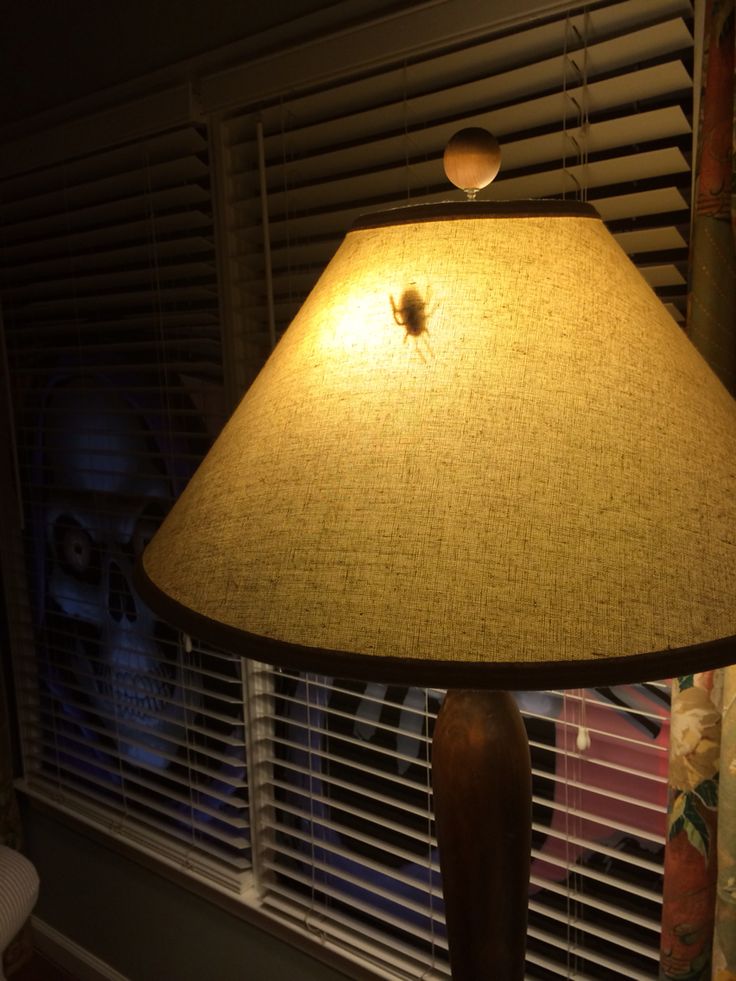
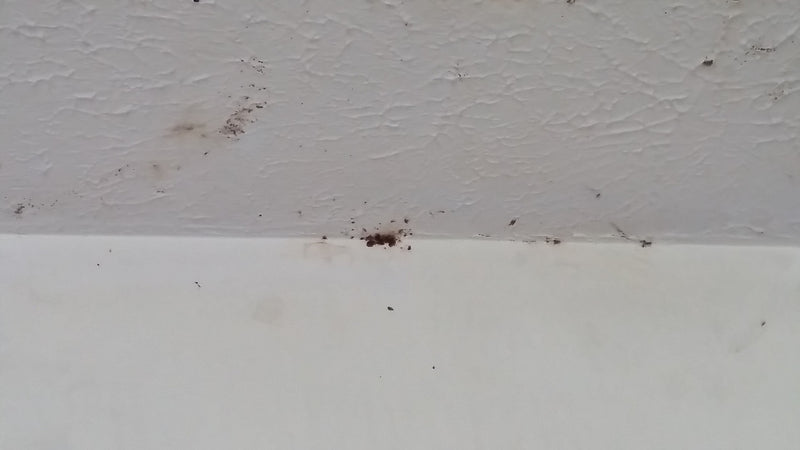
Step2 Inspect Less Common Bed Bug Hiding Spots



Products we recommend for Step 2
How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs
Step1 Preparing a Room for Bed Bug Treatment
Step2 Treat Cracks, Crevices, and Surfaces for Bed Bugs
Products we recommend for Step 2
Step2.1 Treating the Mattress
Products we recommend for Step 2.1
Pro Tip
Step2.2 Treat the Room with Concentrated Insecticide
Products we recommend for Step 2.2
Pro Tip
Step2.3 Use Bed Bug Aerosol Sprays
Products we recommend for Step 2.3
Step2.4 Apply Bed Bug Dust for Long-Lasting Protection
Products we recommend for Step 2.4
Step3 Kill Live Bed Bugs
Step4 Consistency is Key: Repeat Your Treatment
Products we recommend for Step 4
How to Prevent Bed Bugs
Step1 How to Identify Bed Bugs