Ant Identification Guide
Learn How To Identify Ants
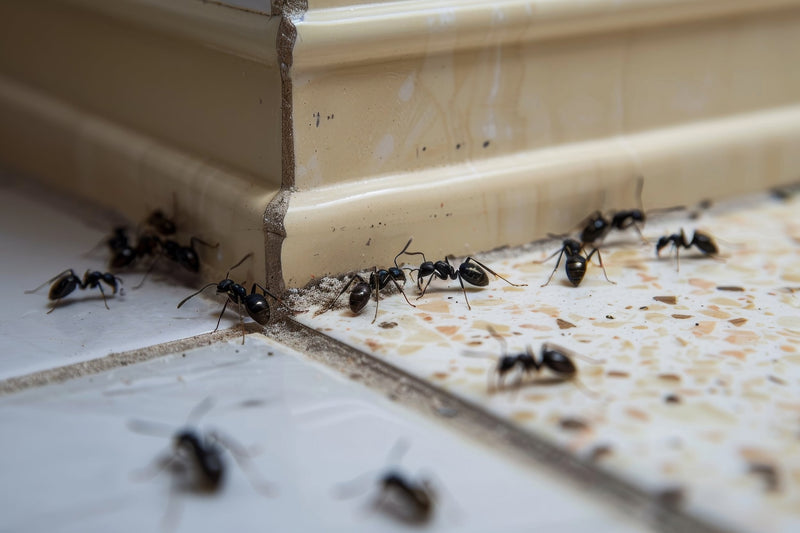

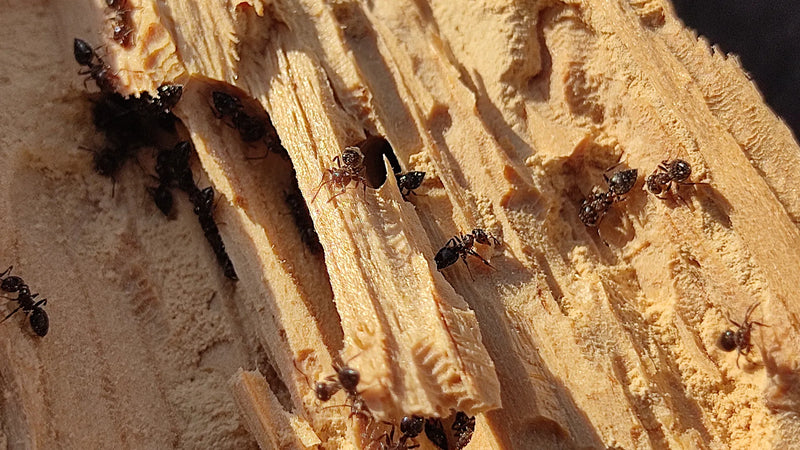
Ants vs. Termites

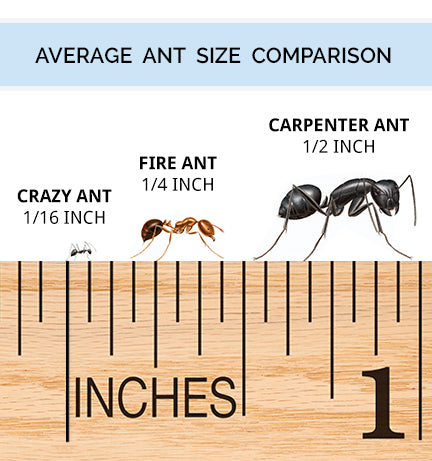
Size
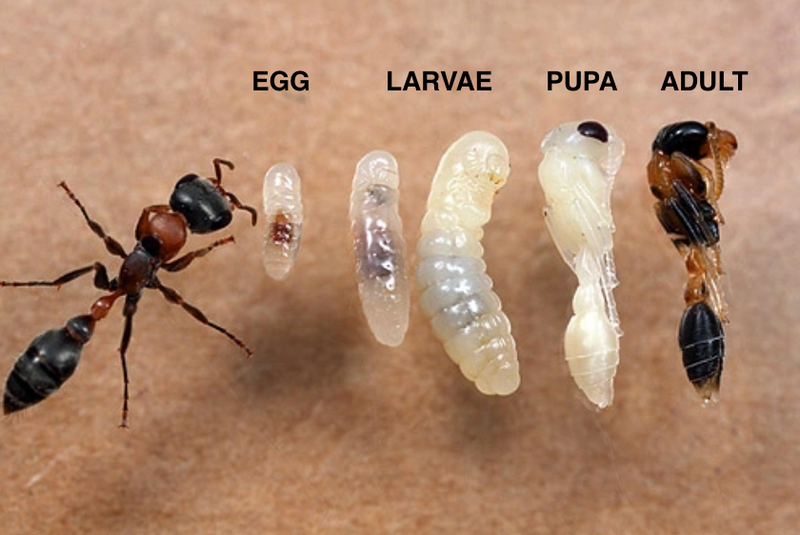
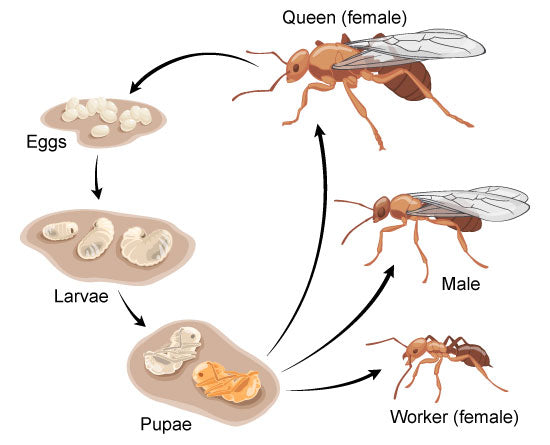

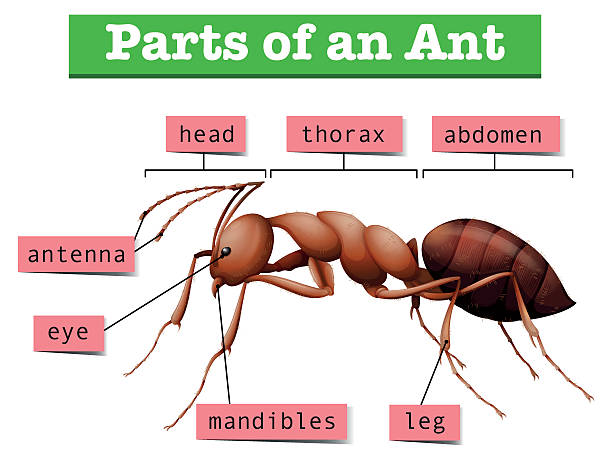
Shape
Color
Range
Acrobat Ants
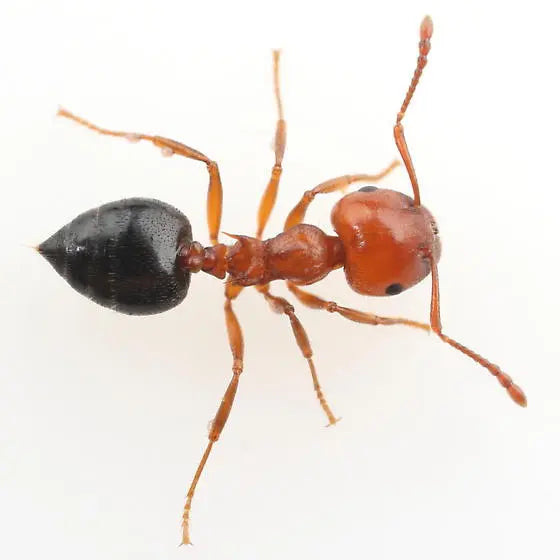
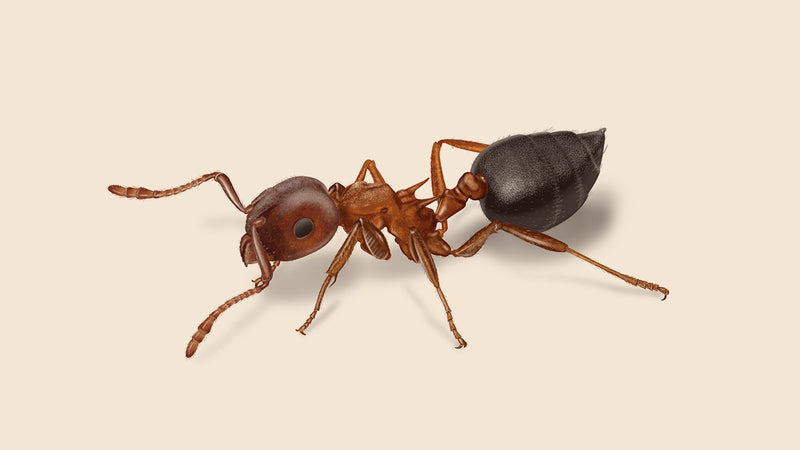



Argentine Ants
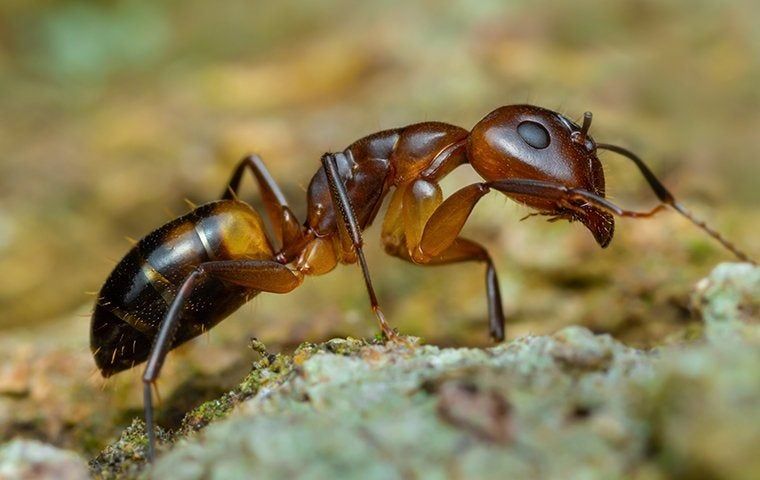
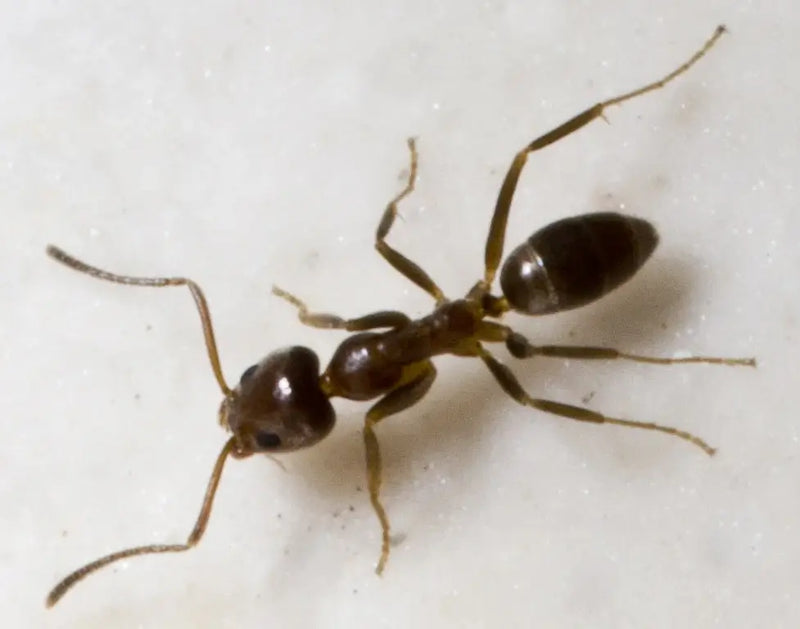
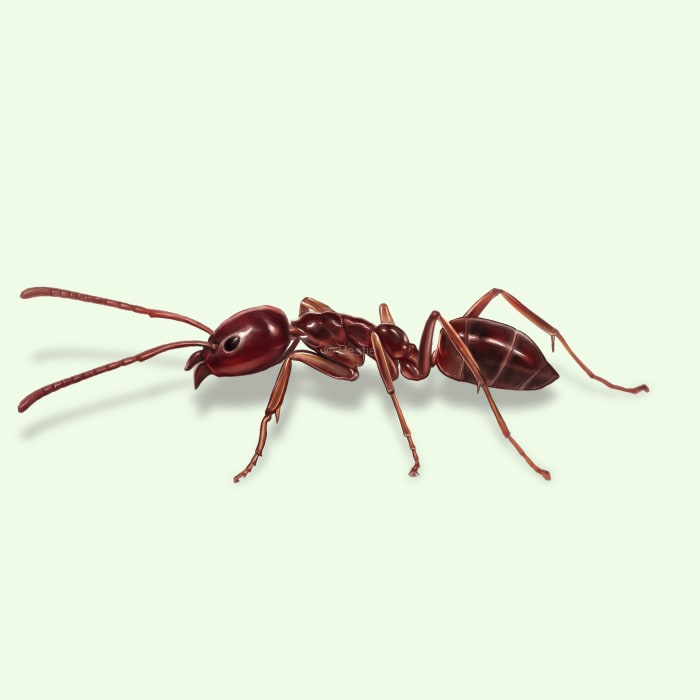



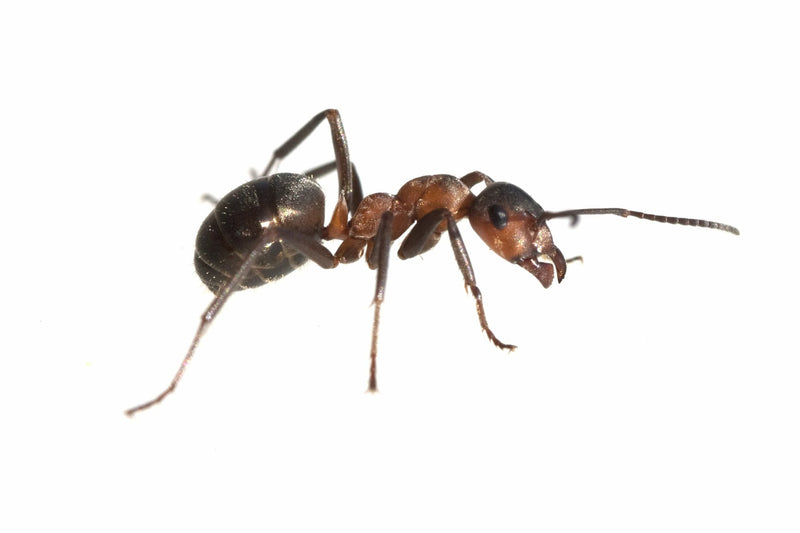
Carpenter Ants
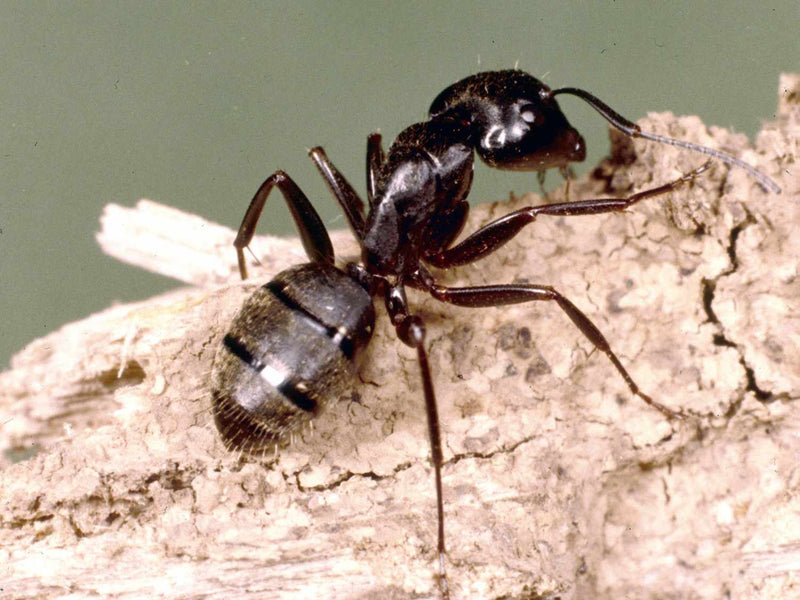
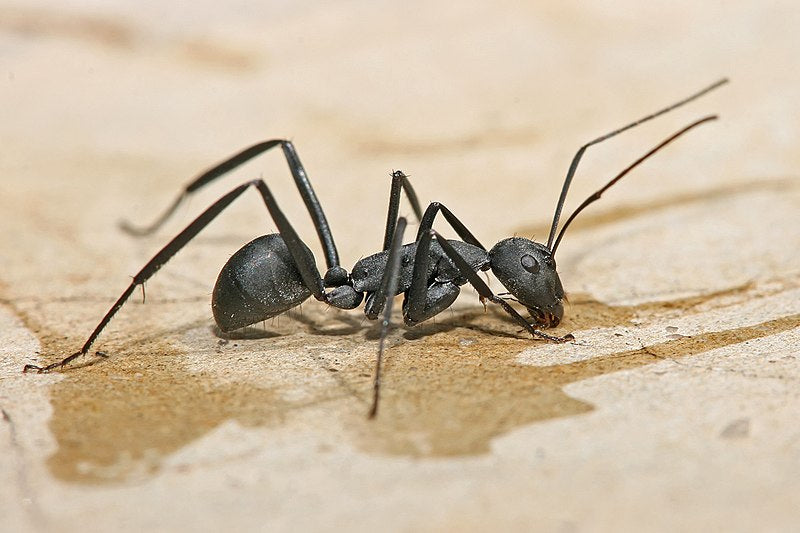
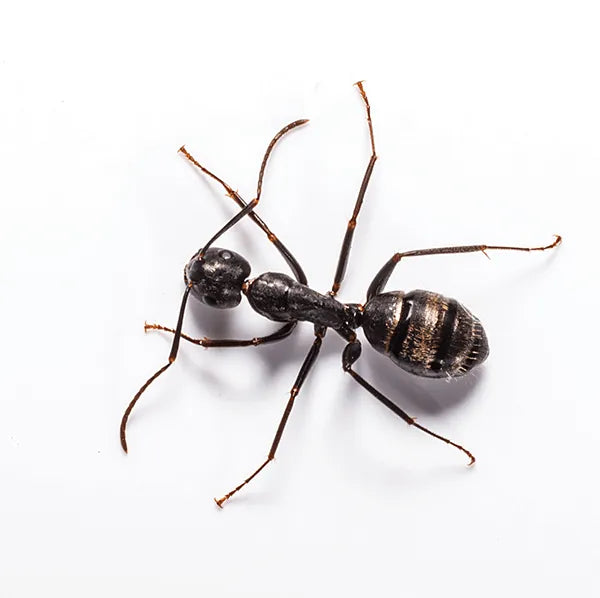



Crazy Ants



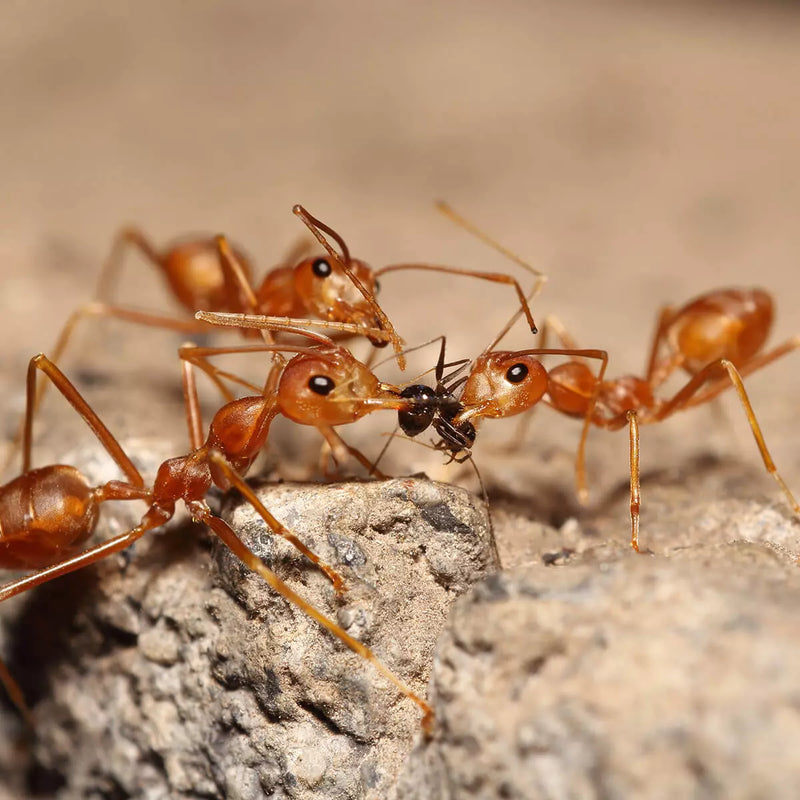
Fire Ants
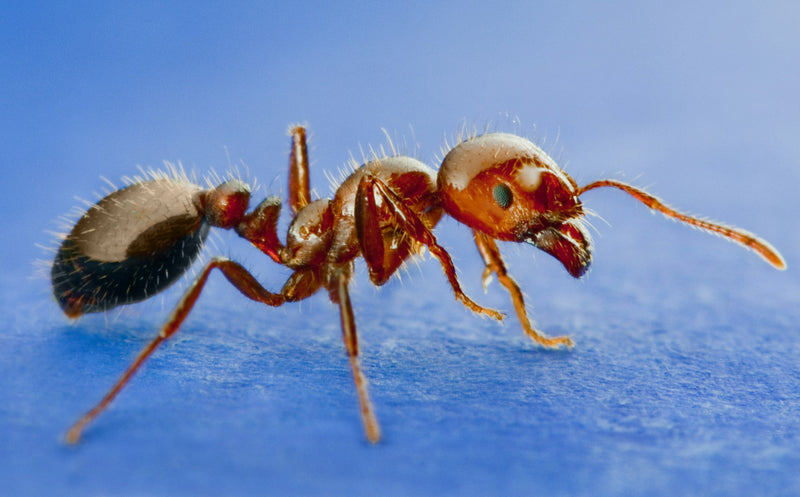
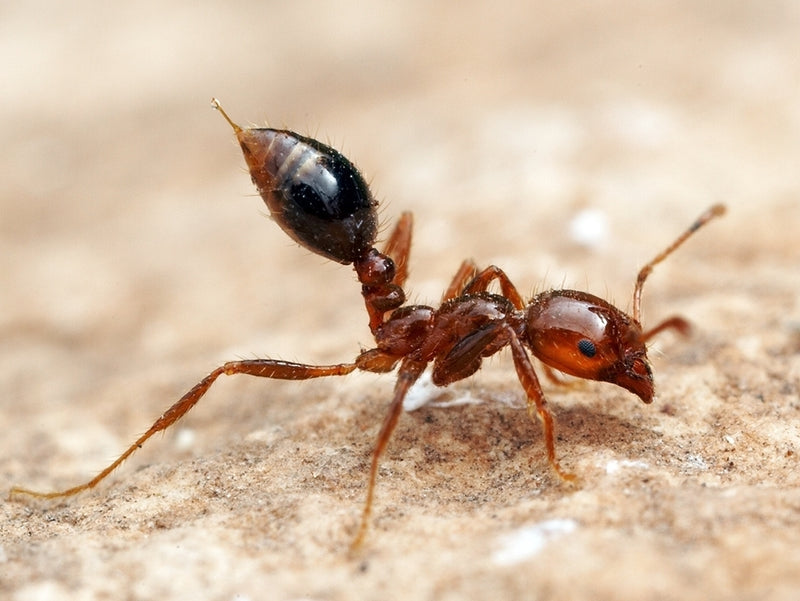



Ghost Ants
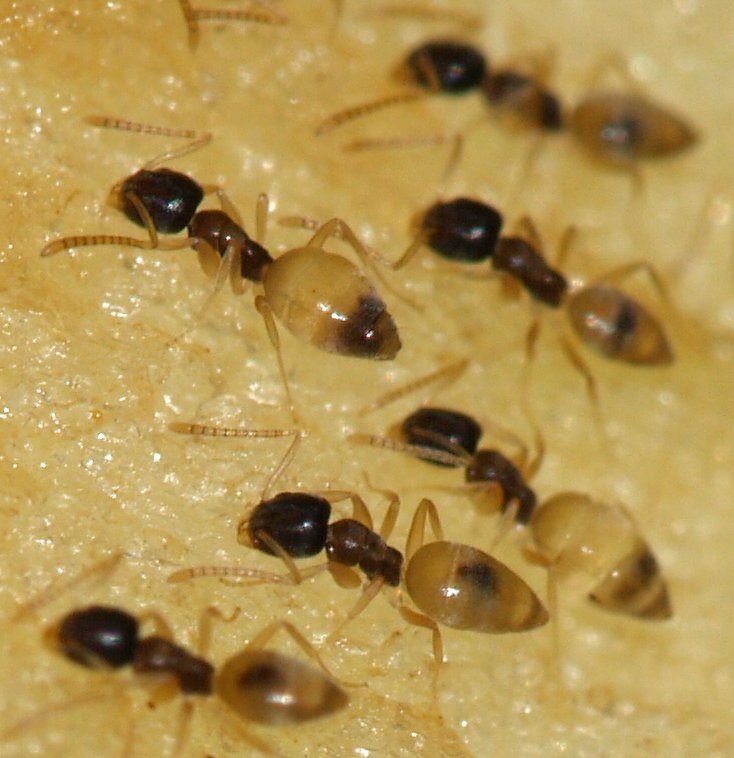
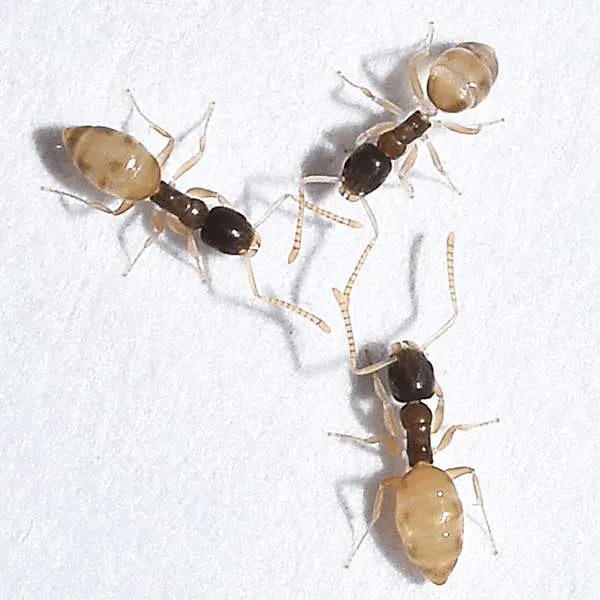
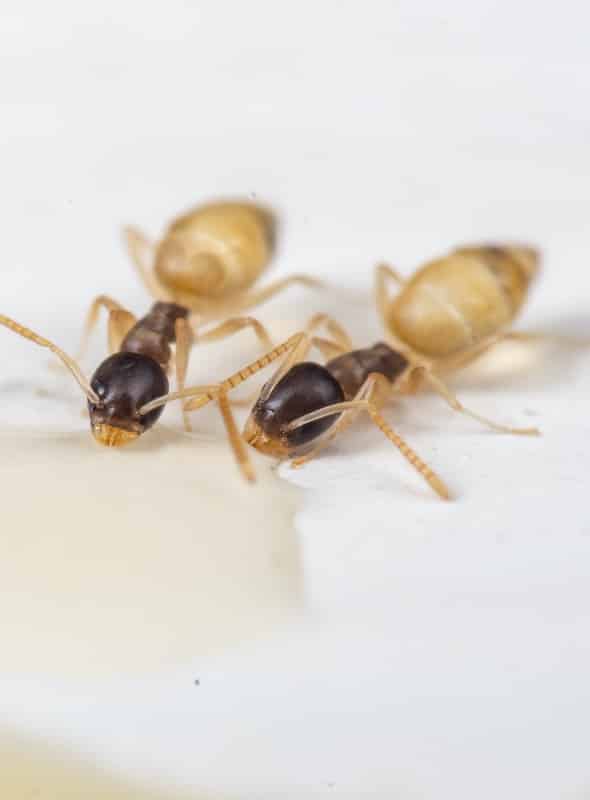



Little Black Ants
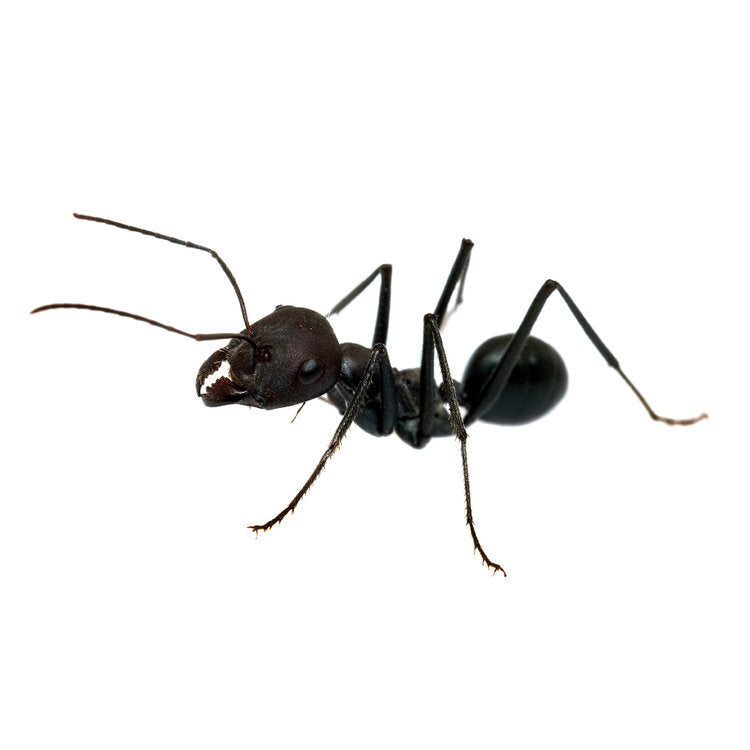
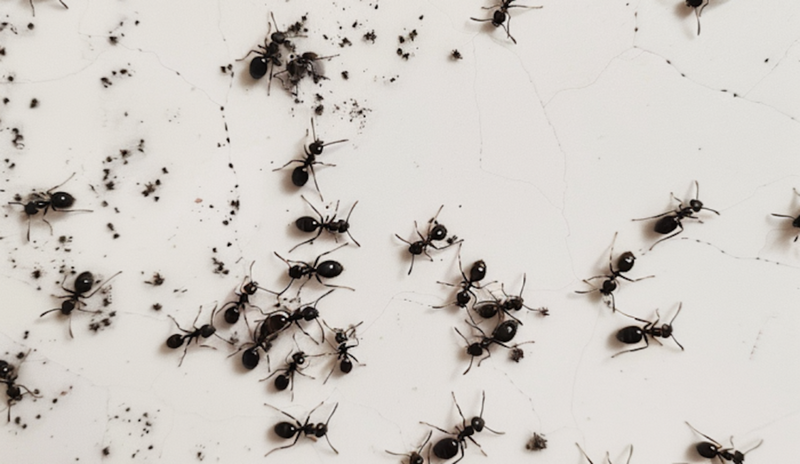
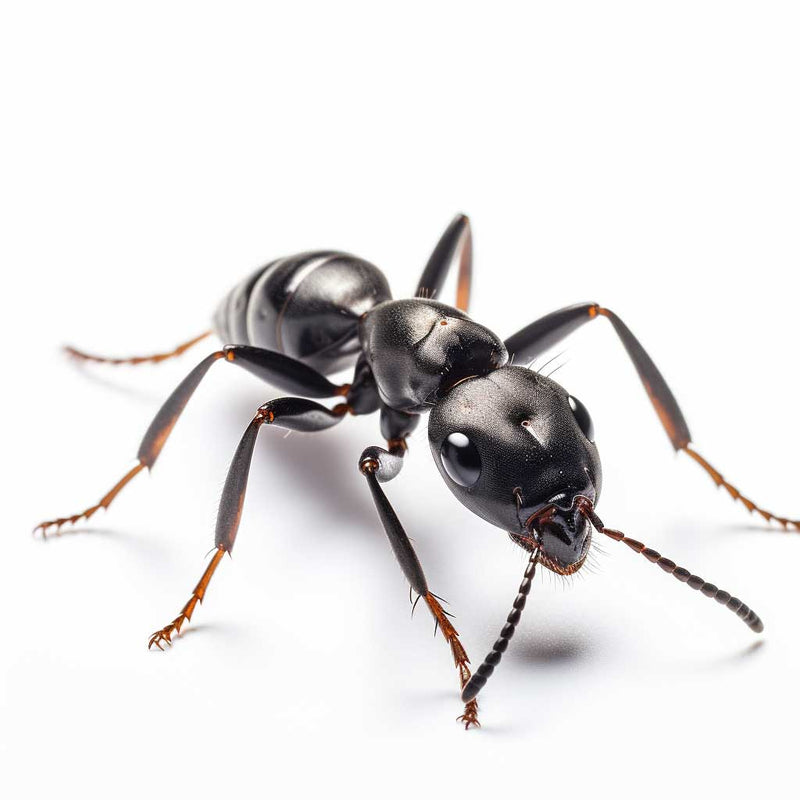



Odorous House Ants
Pavement Ants
Pharaoh Ants
Thief Ants
White-Footed Ants
Ant Inspection Guide
How to Locate Ants and Their Nesting Areas
Inspecting Indoors

Pro Tip
Inspecting Outdoors